# Solidity极简入门: 27. ABI编码解码
我最近在重新学solidity,巩固一下细节,也写一个“Solidity极简入门”,供小白们使用(编程大佬可以另找教程),每周更新1-3讲。
欢迎关注我的推特:@0xAA_Science (opens new window)
欢迎加入WTF科学家社区,内有加微信群方法:链接 (opens new window)
所有代码和教程开源在github(1024个star发课程认证,2048个star发社群NFT): github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity (opens new window)
ABI (Application Binary Interface,应用二进制接口)是与以太坊智能合约交互的标准。数据基于他们的类型编码;并且由于编码后不包含类型信息,解码时需要注明它们的类型。
Solidity中,ABI编码有4个函数:abi.encode, abi.encodePacked, abi.encodeWithSignature, abi.encodeWithSelector。而ABI解码有1个函数:abi.decode,用于解码abi.encode的数据。这一讲,我们将学习如何使用这些函数。
# ABI编码
我们将用编码4个变量,他们的类型分别是uint256, address, string, uint256[2]:
uint x = 10;
address addr = 0x7A58c0Be72BE218B41C608b7Fe7C5bB630736C71;
string name = "0xAA";
uint[2] array = [5, 6];
# abi.encode
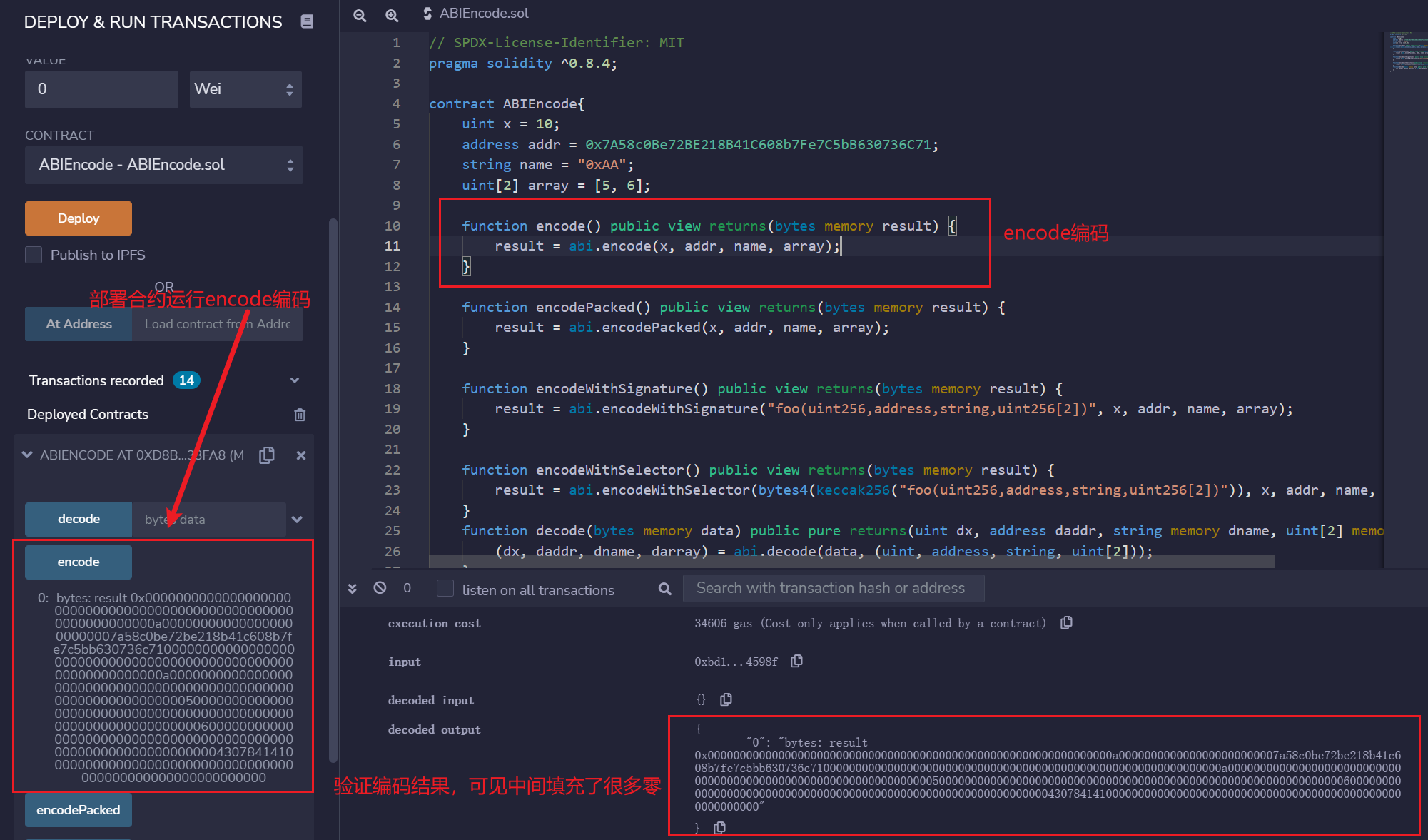
将给定参数利用ABI规则 (opens new window)编码。ABI被设计出来跟智能合约交互,他将每个参数转填充为32字节的数据,并拼接在一起。如果你要和合约交互,你要用的就是abi.encode。
function encode() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encode(x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,由于abi.encode将每个数据都填充为32字节,中间有很多0。
# abi.encodePacked
将给定参数根据其所需最低空间编码。它类似 abi.encode,但是会把其中填充的很多0省略。比如,只用1字节来编码uint类型。当你想省空间,并且不与合约交互的时候,可以使用abi.encodePacked,例如算一些数据的hash时。
function encodePacked() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodePacked(x, addr, name, array);
}
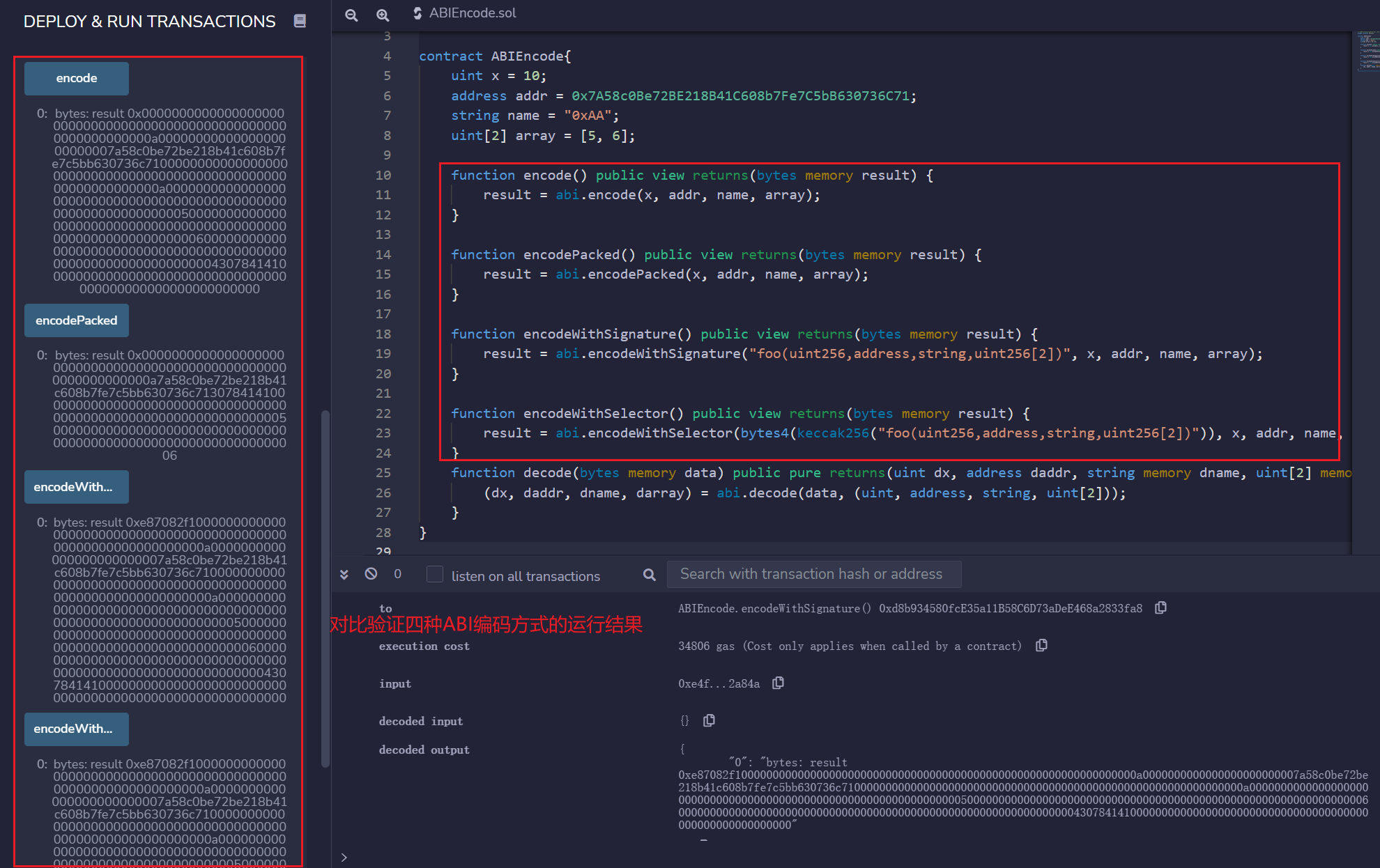
编码的结果为0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a7a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c713078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000050000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006,由于abi.encodePacked对编码进行了压缩,长度比abi.encode短很多。
# abi.encodeWithSignature
与abi.encode功能类似,只不过第一个参数为函数签名,比如"foo(uint256,address)"。当调用其他合约的时候可以使用。
function encodeWithSignature() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodeWithSignature("foo(uint256,address,string,uint256[2])", x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0xe87082f1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,等同于在abi.encode编码结果前加上了4字节的函数选择器[^说明]。
[^说明]: 函数选择器就是通过函数名和参数进行签名处理(Keccak–Sha3)来标识函数,可以用于不同合约之间的函数调用
# abi.encodeWithSelector
与abi.encodeWithSignature功能类似,只不过第一个参数为函数选择器,为函数签名Keccak哈希的前4个字节。
function encodeWithSelector() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodeWithSelector(bytes4(keccak256("foo(uint256,address,string,uint256[2])")), x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0xe87082f1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,与abi.encodeWithSignature结果一样。
# ABI解码
# abi.decode
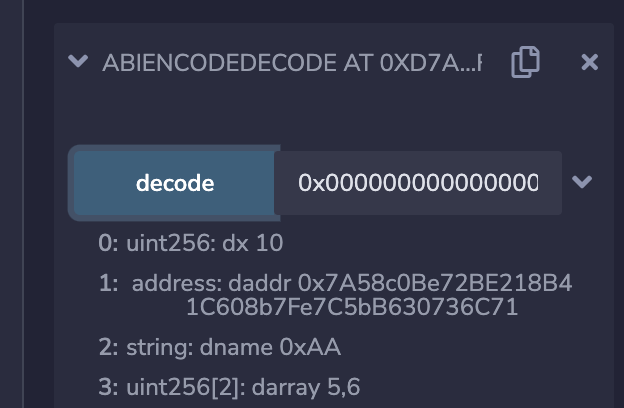
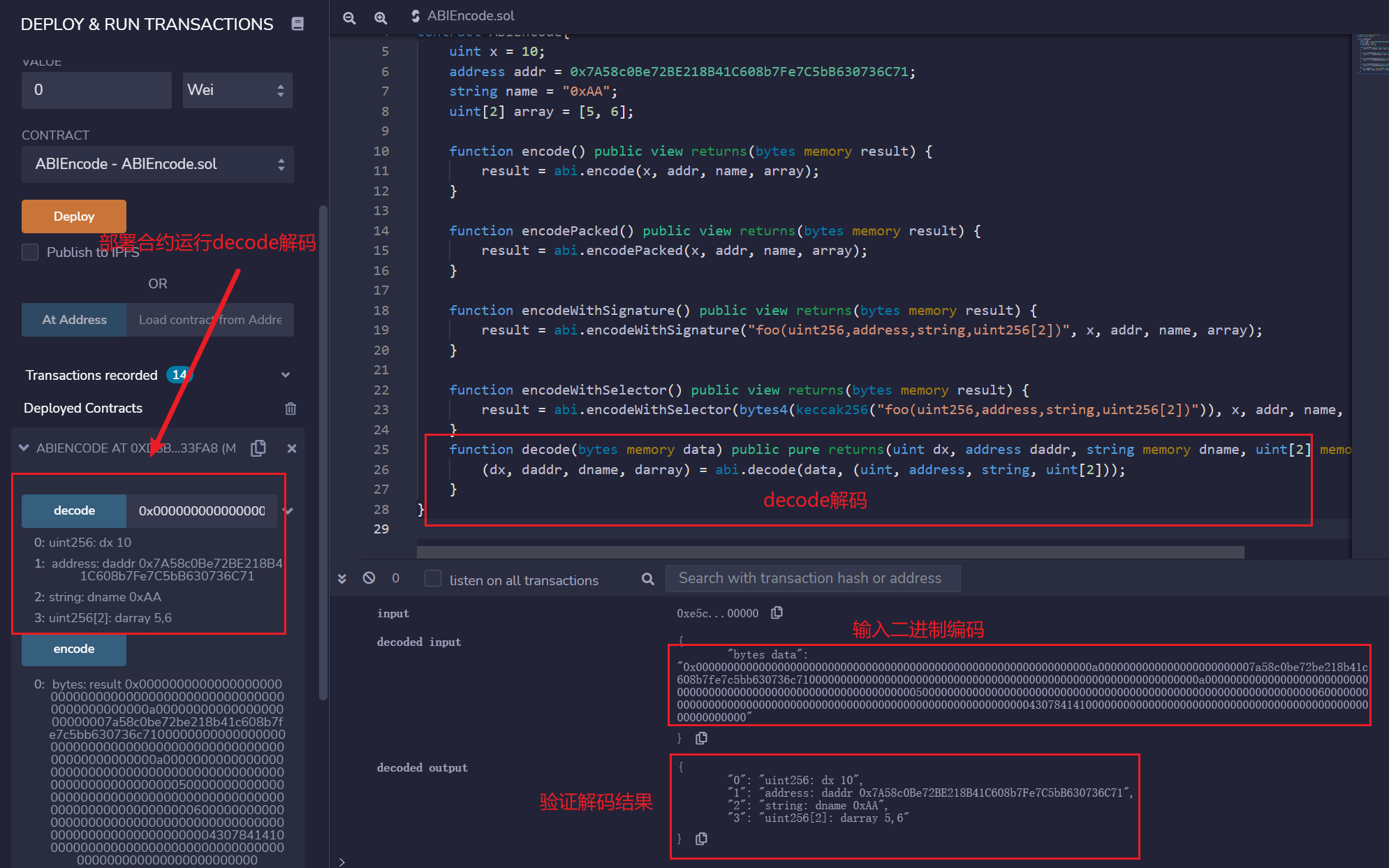
abi.decode用于解码abi.encode生成的二进制编码,将它还原成原本的参数。
function decode(bytes memory data) public pure returns(uint dx, address daddr, string memory dname, uint[2] memory darray) {
(dx, daddr, dname, darray) = abi.decode(data, (uint, address, string, uint[2]));
}
我们将abi.encode的二进制编码输入给decode,将解码出原来的参数:
# 在remix上验证
部署合约查看abi.encode方法的编码结果
对比验证四种编码方法的异同点
查看abi.decode方法的解码结果
# ABI的使用场景
- 在合约开发中,ABI常配合call来实现对合约的底层调用。
bytes4 selector = contract.getValue.selector;
bytes memory data = abi.encodeWithSelector(selector, _x);
(bool success, bytes memory returnedData) = address(contract).staticcall(data);
require(success);
return abi.decode(returnedData, (uint256));
- ethers.js中常用ABI实现合约的导入和函数调用。
const wavePortalContract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, contractABI, signer);
/*
* Call the getAllWaves method from your Smart Contract
*/
const waves = await wavePortalContract.getAllWaves();
# 总结
在以太坊中,数据必须编码成字节码才能和智能合约交互。这一讲,我们介绍了4种abi编码方法和1种abi解码方法。