# Solidity Minimalist Tutorial: 6. Reference Type, Array & Struct
Recently, I have been relearning Solidity, consolidating the finer details, and also writing a "Solidity Minimalist Tutorial" for newbies to learn. Lectures are updated 1~3 times weekly.
Everyone is welcomed to follow my Twitter: @0xAA_Science (opens new window)
WTF Academy Discord: Link (opens new window)
All codebase and tutorial notes are open source and available on GitHub (At 1024 repo stars, course certification is unlocked. At 2048 repo stars, community NFT is unlocked.): github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity (opens new window)
In this lecture, we will introduce two important variable types in Solidity: array and struct.
# Array
An array is a variable type commonly used in Solidity to store a set of data (integers, bytes, addresses, etc.).
There are two types of arrays: fixed-length arrays and variable-length arrays.:
- Fixed-length arrays: Specify the length of the array at the time of declaration. An
arrayis declared in the formatT[k], whereTis the type of the element andkis the length.
// fixed-length array
uint[8] array1;
byte[5] array2;
address[100] array3;
- Variable-length array(Dynamic Array):Length of the array is not specified during declaration. Uses the format of
T[], whereTis the type of the element.bytesis special case, it is an array but you don't need to add[].
// variable-length array
uint[] array4;
byte[] array5;
address[] array6;
bytes array7;
# Rules for creating arrays
In Solidity, there are some rules for creating arrays:
- For a
memorymodifieddynamic array, it can be created with thenewoperator, but the length must be declared, and the length cannot be changed after the declaration. For example:
// memory dynamic array
uint[] memory array8 = new uint[](5);
bytes memory array9 = new bytes(9);
Array literal are arrays in the form of one or more expressions, and are not immediately assigned to variables; such as
[uint(1),2,3](the type of the first element needs to be declared, otherwise the type with the smallest storage space is used by default).When creating a dynamic array, you need an element-by-element assignment.
uint[] memory x = new uint[](3);
x[0] = 1;
x[1] = 3;
x[2] = 4;
# Array member
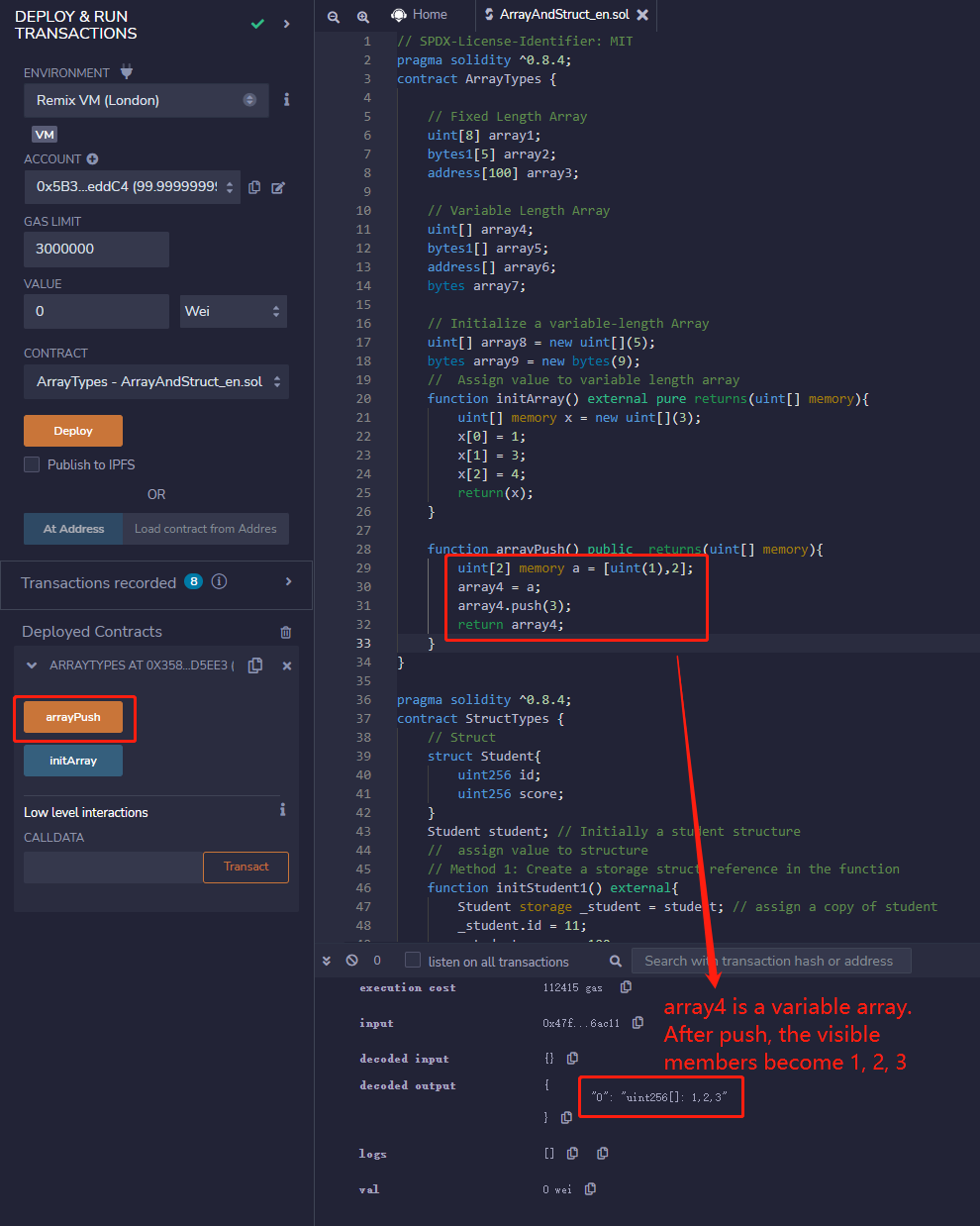
length: Arrays have alengthmember containing the number of elements, and the length of amemoryarray is fixed after creation.push():Dynamic arraysandbyteshave apush()member that adds a0element at the end of the array.push(x):Dynamic arraysandbyteshavepush(x)members, which can add anxelement at the end of the array.pop():Dynamic arraysandbyteshave apop()member that removes the last element of the array.
Example:
# Struct
Dynamic arrays and bytes have a pop() member that removes the last element of the array.
// struct
struct Student{
uint256 id;
uint256 score;
}
Student student; // Initially a student structure
There are two ways to assign values to structures:
// assign value to structure
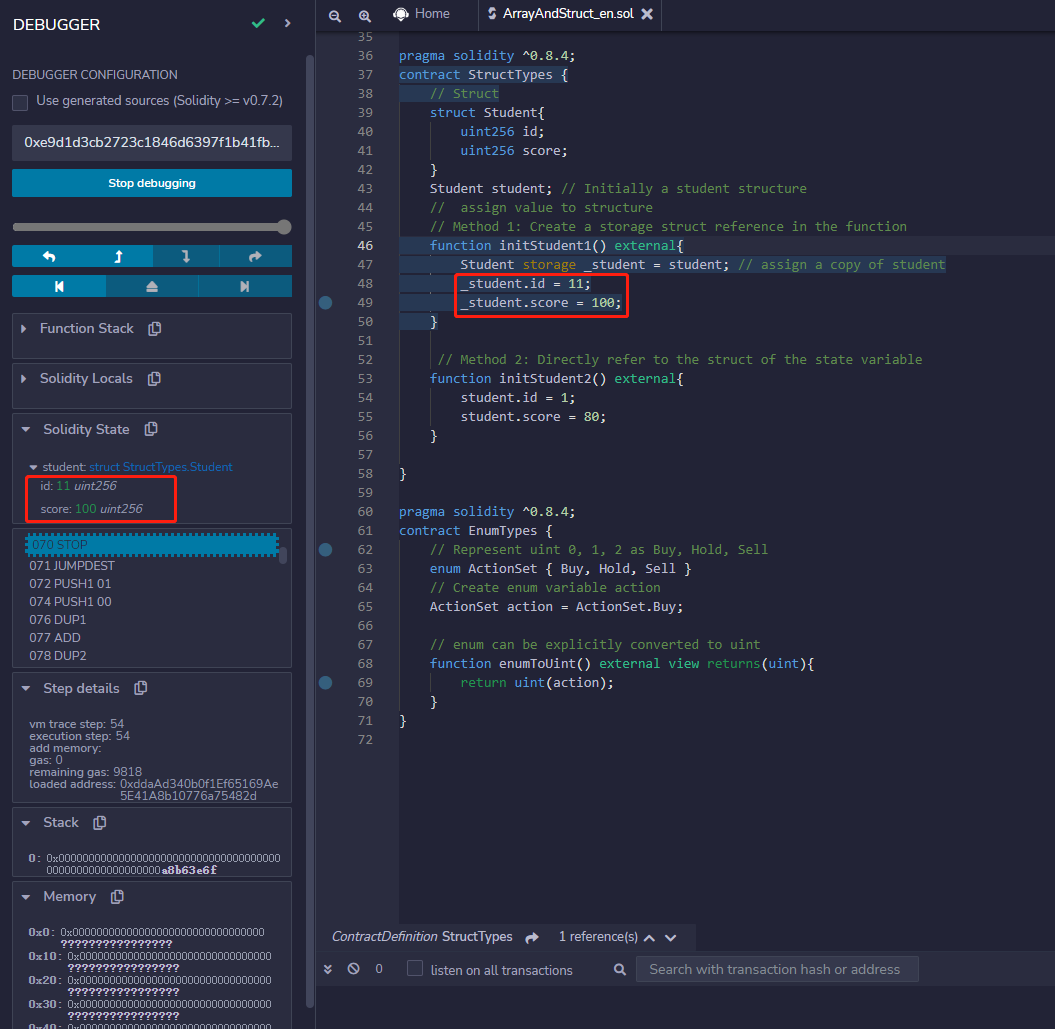
// Method 1: Create a storage struct reference in the function
function initStudent1() external{
Student storage _student = student; // assign a copy of student
_student.id = 11;
_student.score = 100;
}
Example:
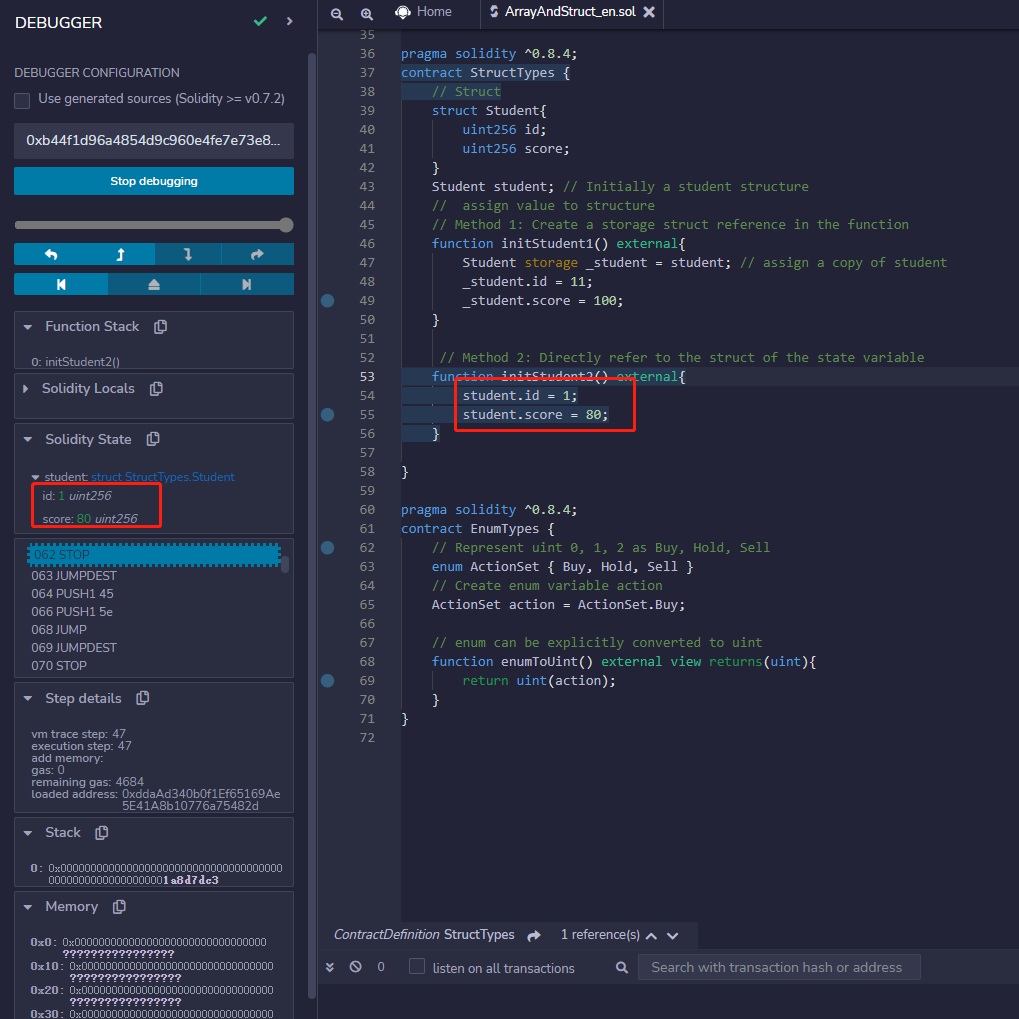
// Method 2: Directly refer to the struct of the state variable
function initStudent2() external{
student.id = 1;
student.score = 80;
}
Example:
# Summary
In this lecture, we introduced the basic usage of array (array) and structure (struct) in Solidity. In the next lecture, we will introduce the hash table in Solidity - mapping (mapping)。