# Solidity Minimalist Tutorial: 9. Constant and Immutable
Recently, I have been relearning Solidity, consolidating the finer details, and also writing a "Solidity Minimalist Tutorial" for newbies to learn. Lectures are updated 1~3 times weekly.
Everyone is welcomed to follow my Twitter: @0xAA_Science (opens new window)
WTF Academy Discord: Link (opens new window)
All codebase and tutorial notes are open source and available on GitHub (At 1024 repo stars, course certification is unlocked. At 2048 repo stars, community NFT is unlocked.): github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity (opens new window)
In this section, we will introduce two keywords in Solidity, constant and immutable. After the state variable declares these two keywords, you cannot change the values after the contract is compiled and it will help to save on gas. In addition, only the numeric variables can declare them as constant and immutable; the string and bytes variables can be declared as constant, but not as immutable.
# Constant and immutable
# Constant
The constant variable must be initialized when declared and cannot be changed after that. Any attempt at changes will cause the contract to fail its compilation step.
// The constant variable must be initialized when declared and cannot be changed after that
uint256 constant CONSTANT_NUM = 10;
string constant CONSTANT_STRING = "0xAA";
bytes constant CONSTANT_BYTES = "WTF";
address constant CONSTANT_ADDRESS = 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000;
# Immutable
The immutable variable can be initialized at declaration or in the constructor, so it is more flexible to work with.
// The immutable variable can be initialized in the constructor and cannot be changed later
uint256 public immutable IMMUTABLE_NUM = 9999999999;
address public immutable IMMUTABLE_ADDRESS;
uint256 public immutable IMMUTABLE_BLOCK;
uint256 public immutable IMMUTABLE_TEST;
You can initialize the immutable variable using a global variable such as address(this), block.number, or a custom function. In the following example, we use the test() function to initialize the IMMUTABLE_TEST variable to a value of 9:
// The immutable variables are initialized with constructor, so that could use
constructor(){
IMMUTABLE_ADDRESS = address(this);
IMMUTABLE_BLOCK = block.number;
IMMUTABLE_TEST = test();
}
function test() public pure returns(uint256){
uint256 what = 9;
return(what);
}
# Verify on Remix
After the contract is deployed, initialized values of the
constantandimmutablevariables can be obtained through thegetterfunction on the Remix.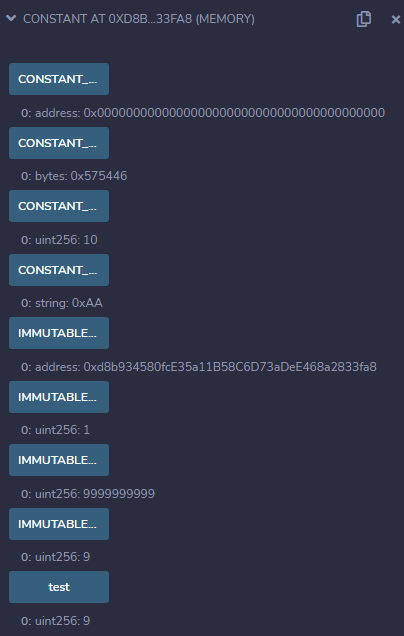
After the
constantvariable is initialized, the contract cannot be compiled if there is an attempt to change its value and the compiler will issue an error ofTypeError: Cannot assign to a constant variable.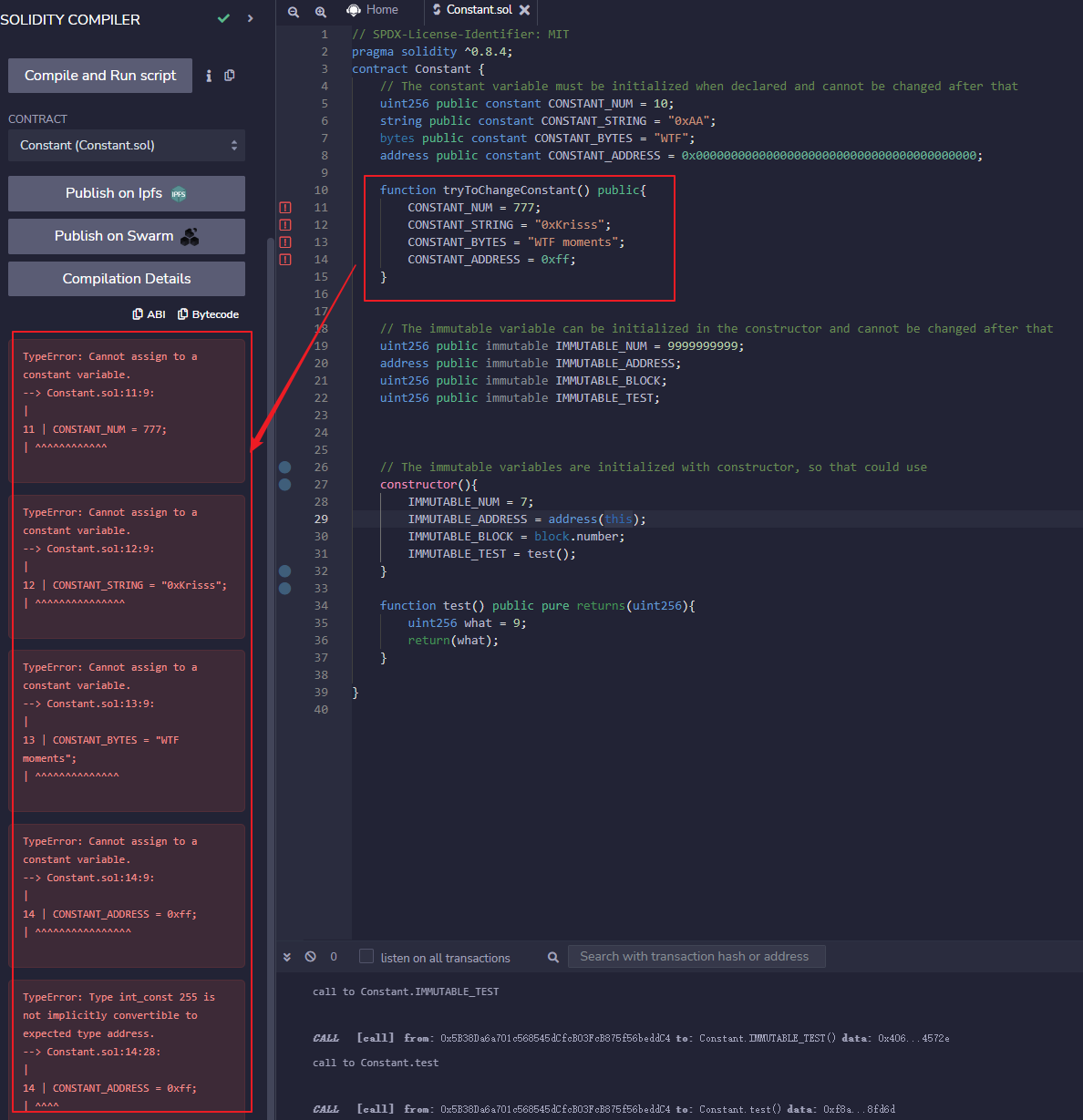
After the
immutablevariable is initialized, the contract cannot be compiled if there is an attempt to change its value and the compiler will issue an error ofTypeError: Immutable state variable already initialized.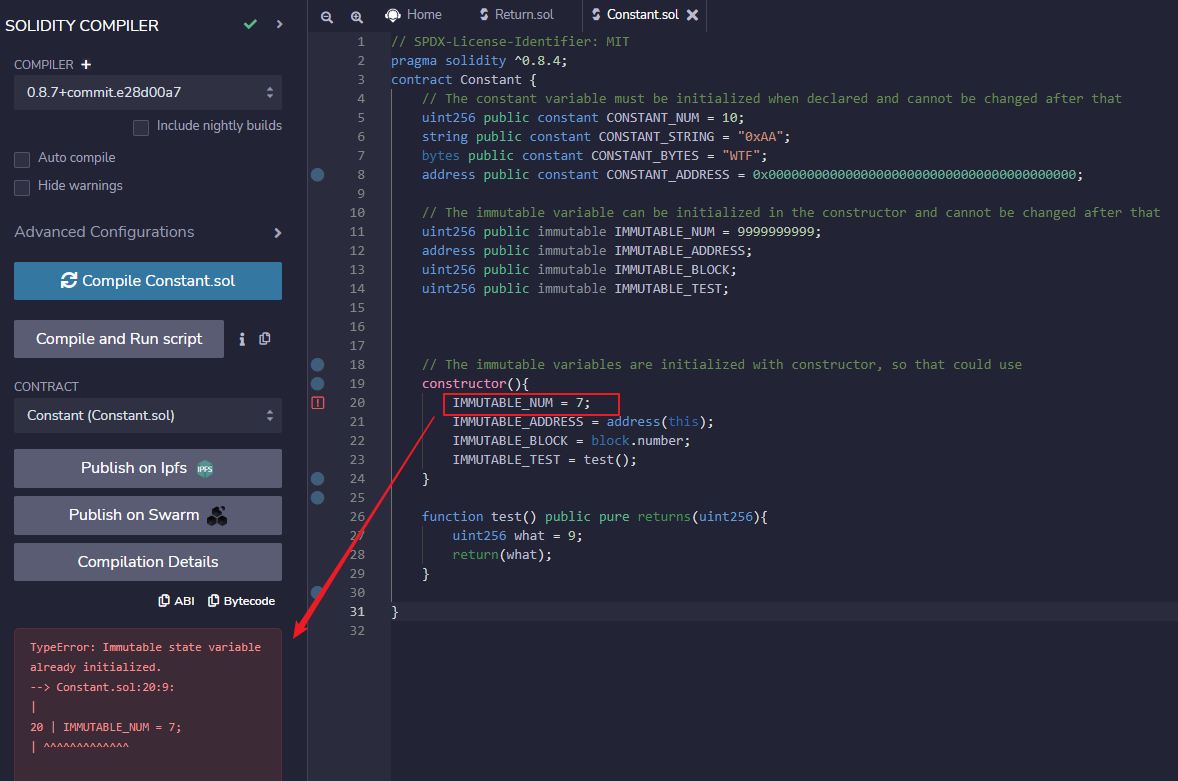
# Summary
In this section, we introduced two keywords in Solidity, constant and immutable, to keep the variables that should not be changed. It will help to save gas while improving the contract's security.