# Solidity Minimalist Tutorial: 2. Value Types
Recently, I have been relearning Solidity, consolidating the finer details, and also writing a "Solidity Minimalist Tutorial" for newbies to learn. Lectures are updated 1~3 times weekly.
Everyone is welcomed to follow my Twitter: @0xAA_Science (opens new window)
WTF Academy Discord: Link (opens new window)
All codebase and tutorial notes are open source and available on GitHub (At 1024 repo stars, course certification is unlocked. At 2048 repo stars, community NFT is unlocked.): github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity (opens new window)
# Types of variables in Solidity
Value Type:This include Boolean, integer, etc. data types, which the variables of these types will always be passed by value (i.e. they are always copied when they are used as function arguments or in assignments).
Reference Type:This includes arrays and structs, which take up a large amount of storage space and pass addresses (i.e. like a pointers) directly when values are assigned.
Mapping Type: These are similar to hash tables for Solidity.
Function Type:The Solidity documentation classifies functions into numeric types, but I think they are very different from the other types mentioned, so I will classify them separately.
Only the more commonly used value types will be introduced in this primer. The uncommon value types will not be discussed as it is not widely used. This tutorial, Tutorial 2, will introduce numeric types, while Tutorial 3 will introduce function types, and Tutorial 4 will introduce reference type and mapping type.
# Numeric type
# 1. Boolean
Boolean data type is a binary variable,either a value of true or false.
// Boolean
bool public _bool = true;
Operators for Boolean data type include:
- ! (logical NOT)
- && (logical AND)
- || (logical OR)
- == (equality)
- != (inequality)
Code:
// Boolean operators
bool public _bool1 = !_bool; // logical NOT
bool public _bool2 = _bool && _bool1; // logical AND
bool public _bool3 = _bool || _bool1; // logical OR
bool public _bool4 = _bool == _bool1; // equality
bool public _bool5 = _bool != _bool1; // inequality
From the above source code:the value of the variable _bool is true;so _bool1 is not_bool,which yields false;_bool && _bool1's value is false;_bool || _bool1's value is true;_bool == _bool1's value is false;and _bool != _bool1's value is true.
Important note: The && and || operator follows a short-circuit evaluation rule. This means that for an expression such as f(x) || g(y),if f(x) is true,then g(y) will not be computed; even if its result is the opposite of f(x).
# 2. Integers
Integers are the whole numbers in Solidity,most frequently used examples include:
// Integer
int public _int = -1; // integers including negative numbers
uint public _uint = 1; // positive numbers
uint256 public _number = 20220330; // 256-bit positive integers
Some commonly used integer operators include:
- Inequality operator(which returns a Boolean value):
<=,<,==,!=,>=,> - Arithmetic operator:
+,-, unary operators-,+,*,/,%(modulo),**(exponent)
Code:
// Integer operators
uint256 public _number1 = _number + 1; // +,-,*,/
uint256 public _number2 = 2**2; // Exponent
uint256 public _number3 = 7 % 2; // Modulo (Modulus)
bool public _numberbool = _number2 > _number3; // Great than
You can try running these code and see the results of these 4 variables. Correct answers get a POAP, maybe?
# 3. Addresses
Address type stores a 20-bit value (similar to the size of an Ethereum address). Address types also have a member variable (members of address) which serve as the basis for all contracts. There are ordinary addresses and addresses that can transfer 'ETH' ('payable'). The 'payable' address has two members, 'balance()' and 'tranfer()', making it easy to check 'ETH' balances and transfer funds.
Code:
// Address
address public _address = 0x7A58c0Be72BE218B41C608b7Fe7C5bB630736C71;
address payable public _address1 = payable(_address); // payable address (can transfer fund and check balance)
// Members of address
uint256 public balance = _address1.balance; // balance of address
The next tutorial (Tutorial 3) on function type will teach you how to use these address types.
# 4. Fixed-size byte arrays
There are two types of byte arrays (bytes), one is fixed of length (byte, bytes8, bytes32), and the other is without a fixed length. The fixed length belongs to the numeric type, and the non-fixed length type is the reference type (to be introduced in Tutorial 4). The fixed length bytes can store data, and consumes less gas.
Code:
// Fixed-size byte arrays
bytes32 public _byte32 = "MiniSolidity";
bytes1 public _byte = _byte32[0];
The 'MiniSolidity' value is stored in the form of bytes into the variable _byte32. If converted to 'hexadecimal' format the output is as follows: 0x4d696e69536f6c69646974790000000000000000000000000000000000000000
On the other hand, the _byte variable stores the first byte of the _byte32 variable, which is 0x4d.
# 5. Enumeration
Enumeration(enum)is a user-defined data type within Solidity. It is mainly used to assign names to the uint data type, which keeps the program easy to maintain and read. It is similar to enum in the C language, with indexation starting at 0 for uint data type.
Code:
// Let uint 0, 1, 2 represent Buy, Hold, Sell
enum ActionSet { Buy, Hold, Sell }
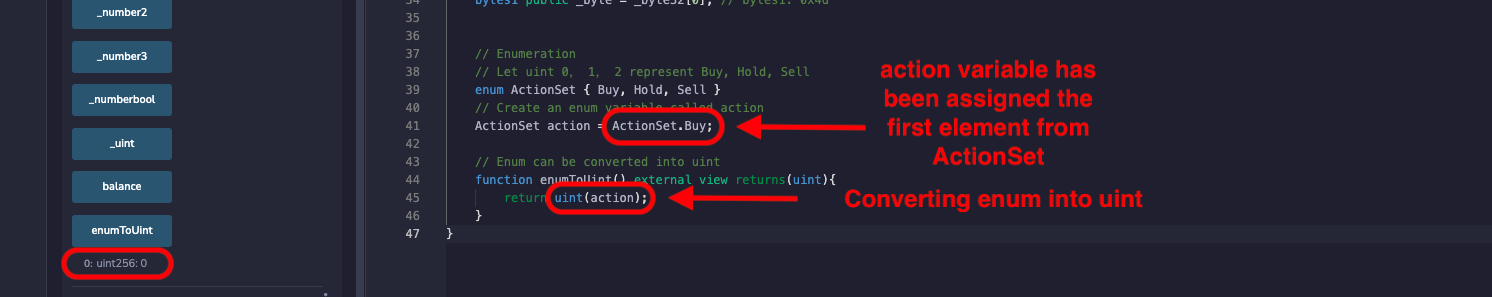
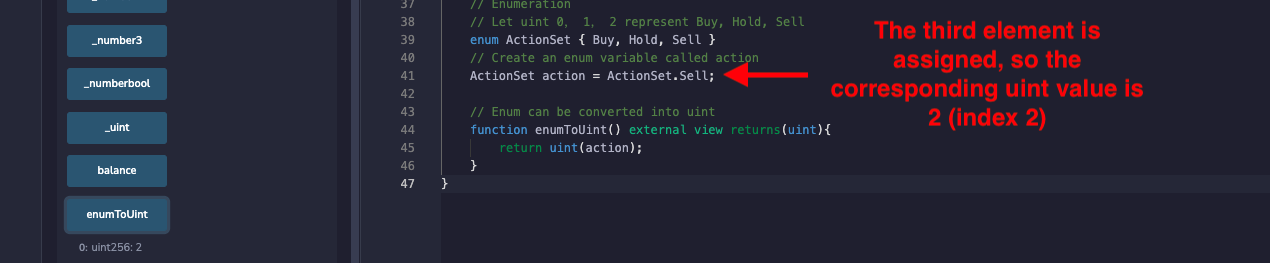
// Create an enum variable called action
ActionSet action = ActionSet.Buy;
It can be converted interchangeably to uint data type and checks whether the converted positive integer is within the length of the enumeration, otherwise it will report an error:
// Enum can be converted into uint
function enumToUint() external view returns(uint){
return uint(action);
}
enum is a less popular class of variable that is hardly used by anyone.
# Example from Remix
After deploying the contract, you can view the specific values of each type of variable
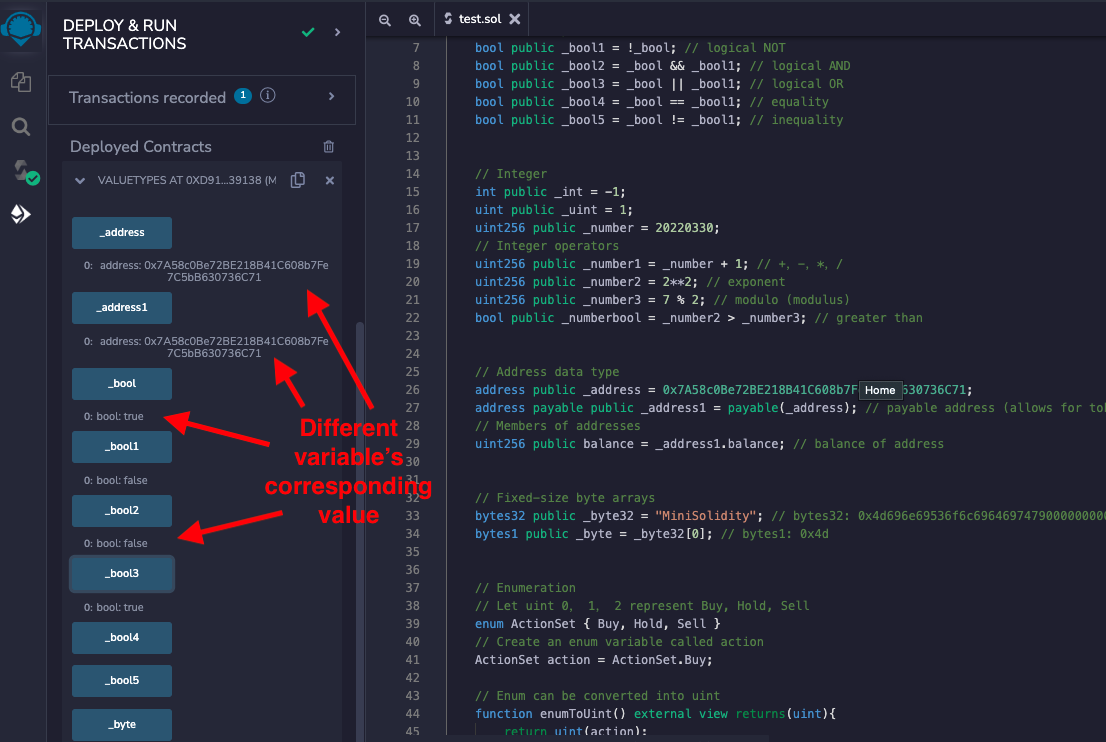
Conversion between enum and uint
# Summary
In the second lecture, we introduce the 4 variable types in Solidity and explained the Boolean, integer, address, fixed-length byte array, and enumeration of numeric variables ('value type'). We will cover several other value types in the subsequent tutorials.